| CAS
NO. |
23964-57-0 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
|
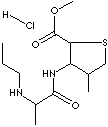
| FORMULA |
C13H20N2O3S·HCl |
| MOL
WT. |
320.84 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2934.90 |
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral
rat LD50: 980mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Ultracaine; Articaine
HCl; |
| 4-methyl-3-(2-(propylamino)propionamido)-2-Thiophenecarboxylic acid, methyl
ester, monohydrochloride;
4-Methyl-3-(2-(propylamino)propion amido)- 2-Thiophenecarboxylic acid methyl ester
HCl; |
|
SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
White
crystalline powder, odourless |
| MELTING
POINT |
|
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
soluble
|
| pH |
4
- 5 |
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
| Local anesthetic is a substance that causes loss of sensation only to the area
to which it is applied without affecting consciousness. Most local anesthetics
structures have amino-ester or an amino-amide group which are linked to
hydrophilic (secondary or tertiary amine) and to hydrophobic group (aromatics)
on the other sid. The ester can be hydrolysed in plasma by the enzyme pseudocholinesterase into para-aminobenzoic
acid. Amide is stable for longer
acting and more systemic distribution. Ester types include Procaine (Novocain),
Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine), Cocaine, Tetracaine (Pontocaine), Benzocaine,
Tetracaine. Amide types include Lidocaine (Xylocaine), Mepivacaine(Carbocaine),
Prilocaine (Citanest), Bupivacaine (Marcaine), Etidocaine (Duranest). |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
| BP93/USP23 |
|
APPEARANCE
|
White
crystalline powder |
|
ASSAY
|
99.5%
min
|
|
SULFATE
|
0.1%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 26/27/28, Safety
Phrases: 22-36/37/39-45 |
